Troubleshooting

The wiki page covers troubleshooting tips for installation issues, general issues, network issues, and hardware problems.
ISO
[edit]ISO to USB Image Writer Tools
[edit]functional, bootable image:
- Flashing using a Qubes Kicksecure VM with hide hardware information enabled using
cp. - Flashing using a Qubes Kicksecure VM using KDE ISO Image Writer from Flathub.
- Flashing using a Debian VM using the balenaEtcher AppImage.
- Flashing using a Windows OS with the balenaEtcher installer version.
- Flashing using a Windows OS with UNetbootin (portable).
broken:
- Flashing using a Qubes Kicksecure VM with hide hardware information enabled using balenaEtcher, which shows an error message due to hide hardware information.
Tips
[edit]- Practice on a separate notebook.
- Use a VM to flash for security against data loss.
Live ISO Known Issues
[edit]balenaEtcher
[edit]Platform specific.
- A) Non-Windows host operating systems such as macOS or Linux: No special notice.
- B) Windows: See below.
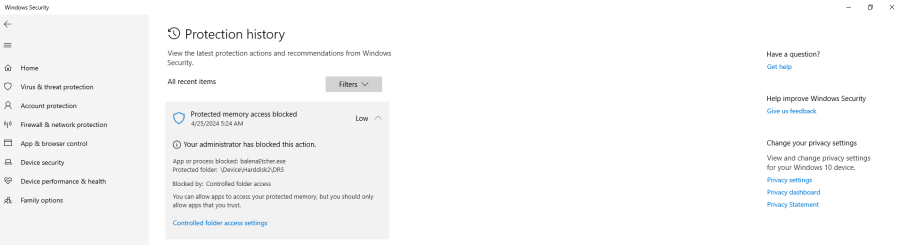
If you have Controlled Folder Access![]()
enabled, you need to allow changes by Etcher:
Figure: Windows Protection History
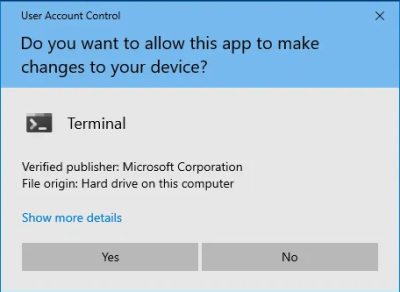
If you have User Account Control![]()
enabled, allow Etcher to make changes to your device by pressing "Yes" when a popup similar to the following appears:
Figure: Windows User Account Control
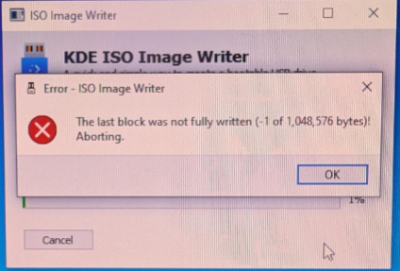
KDE ISO Image Writer
[edit]The last block was not fully written (-1 of 1,048,576 bytes)!KDE ISO Image Writer Error Message
In this case,
- A) try to unmount the USB device first or
- B) use a different ISO Image Writer tool.
DVD Support
[edit]
Untested. Should work in theory. Tested inside QEMU and VirtualBox with an emulated CD-ROM drive. So chances are good that it will work with a real DVD drive as well.
Dual Boot
[edit]It is recommended to physically disconnect any other physical disks while installing Kicksecure (or any other operating system) to mitigate the risk of the installer overwriting the wrong drive due to user error or software bugs.
Fastboot
[edit]Fastboot is a BIOS setting which skips attempting to boot from USB on some computers. In this case, the user must disable Fastboot in order to be able to boot from USB.
Encryption Settings
[edit]- Default Encryption Settings: Which encryption settings will be used? See: cryptsetup luksFormat --help
- Authority: Where are the default encryption settings coming from? From distribution defaults. In this case, from Debian because Kicksecure is based on Debian.
- User customization: No, unfortunately not possible. Full disk encryption settings are not configurable in calamares. calamares upstream bug report

(closed, but not implemented, "patches welcome")
- Alternatives: Distribution Morphing: morphing Debian into Kicksecure
- Forum discussion: ISO - cryptsetup Full Disk Encryption (FDE) - set more secure default encryption settings

Minor Issues
[edit]This might be an issue when installing additional packages while running the live ISO. This will not be an issue after installing to hard drive.
Failed to mount sysroot.mount - /sysroot.
[edit]The message Failed to mount sysroot.mount - /sysroot. during the boot ISO process is only a cosmetic issue. It can be safely ignored.
This issue will be fixed in Kicksecure 18 and above (Debian trixie based).
Details here: https://forums.kicksecure.com/t/iso-error-message-during-boot-mount-sysroot-special-device-liveos-rootfs-does-not-exist/418![]()
update-grub
[edit]Note: There is most likely no need to run the following command. This is only documentation "what if". If running the following command,
sudo update-grub
then the following error message would be shown.
/usr/sbin/grub-probe: error: failed to get canonical path of `LiveOS_rootfs'. zsh: exit 1 sudo update-grub
Please report a bug if this breaks something for you. Adding a workaround for this would not be difficult.
This command is also unrelated to fixing installation issues. Users executing update-grub from an ISO is not very useful because an ISO is a read-only filesystem. Running update-grub can be useful during the installation from ISO to hard drive, but this is something that needs to happen inside a chroot, which is a specifically prepared environment. This is very difficult for most users and unnecessary because this is part of the tasks of the installer.
Calamares ISO Installer
[edit]Calamares ISO Installer - Known Issues
[edit]Calamares ISO Installer - Logs Access
[edit]1 Boot the ISO.
2 Select sysmaint session in the boot menu.
3 Wait for the system to boot.
4 Click Install System.
5 You will briefly see a black terminal window. Then the Calamares window will start.
6 The absence of a taskbar might be confusing.
- A taskbar will be introduced in the next release.
- The terminal window will keep running in the background.
7 Install the system.
8 In the last Calamares screen, make sure to uncheck restart now.
9 Press done.
10 Calamares will close and the install-host terminal window will reappear.
11 To save the log:
Click Terminal -> Save Contents.
Connectivity Troubleshooting
[edit]ICMP Fix
[edit]Therefore no such fix is required yet.
Qubes-specific Connectivity Issue
[edit]Complete the following steps:
- Shut down
kicksecure. - Change the
kicksecureNetVM setting fromsys-firewalltosys-net. - Restart
kicksecure.
This procedure might help, but should not be considered a final solution. [2]
Why can't I Ping the Kicksecure?
[edit]The Kicksecure does not respond to ping or similar commands because it is firewalled for security reasons; see /usr/bin/kicksecure_firewall or refer to the Kicksecure source code. In most cases it is unnecessary to ping the Kicksecure anyhow.
If you insist on pinging the Kicksecure or have a unique setup that requires it, then this can be tested by clearing all firewall rules with the dev_clearnet
script. Alternatively, a script can be run to try and unload / remove every iptables rule, or the Kicksecure firewall can be hacked to not load at all. The latter method is only for experts and it is necessary to comment out exit 0 at the beginning.
General Troubleshooting
[edit]Introduction
[edit]Troubleshooting issues can be time intensive and success cannot be guaranteed. Some users expect Kicksecure to provide an easy experience. While the Kicksecure developers make every effort to meet user expectations, limited funding and human resources make meeting these expectations impossible.
Even though problems emerge when using Kicksecure, the cause is most often unrelated to Kicksecure code. For example, users often report the same Kicksecure release worked on different hardware and/or with a different host operating system. Most software such as the host operating system or the virtualizer is developed by independent entities; this is the norm in Linux distributions. See Linux User Experience versus Commercial Operating Systems to learn more about these relationships, as well as organizational and funding issues in the Open Source ecosystem.
Essential General Troubleshooting Steps
[edit]1. "Forget" about Kicksecure for a moment and imagine you had never heard of the platform. Test your host computer first.
2. Exclude basic hardware issues.
3. Ensure the virtual machine (VM) images have been imported into a supported virtualizer listed on the Download page.
4. Debian (based) Linux host operating system users only: The following command should not show any errors. [3]
sudo dpkg-reconfigure -a
5. Debian (based) Linux host operating system users only: The following command should be silent and not show any errors or output at all. [3]
sudo dpkg --configure -a
6. Debian (based) Linux host operating system users only: Next attempt to retrieve all available updates.
sudo apt update
sudo apt full-upgrade
7. Check for possible Low RAM Issues.
- Free up Additional Memory Resources.
- Also refer to Advice for Systems with Low RAM.
8. Virtualizer-specific troubleshooting.
9. Check if other VMs are functional, such as newly created ones or those from a different vendor.
- "Forget" about Kicksecure for a moment and imagine you had never heard of the platform. Test the virtualizer host software first.
- Try a VM other than Kicksecure such as Debian
trixie. - If the issue persists, this means the root issue is not caused by Kicksecure, see: unspecific to Kicksecure. In this case, attempt to resolve the issue as per Self Support First Policy.
10. Check System Logs.
- Sometimes crashing or freezing issues are easier to detect by Watching Systemd Journal Log of Current Boot.
- Sometimes it is necessary to Check Systemd Journal Log of Previous Boot.
11. If a graphical environment (where one can use a computer mouse) is unavailable after booting, utilize a virtual console to acquire system logs.
- Recovery, Virtual Consoles.
- Check system logs of the previous boot (step 10).
12. Use recovery mode to acquire system logs.
- Boot in recovery mode.
- Check system logs of previous boot (step 10).
13. Use a chroot to acquire system logs.
If a virtual console is inaccessible and recovery mode is also broken, try using a chroot for recovery.
Low RAM Issues
[edit]If insufficient RAM is available for Kicksecure VMs, they might become unusable. Low RAM issues in Kicksecure are commonly caused by:
- Unnecessary processes running and/or multi-tasking on the host OS.
- Multiple, open browser tabs.
- Unnecessary processes running in the Kicksecure VM.
- Allocating more RAM to the Kicksecure VM than is available; this prevents the VM from booting.
- Insufficient RAM allocated to the Kicksecure VM.
- Other non-Kicksecure VMs running in parallel.
Insufficient RAM can cause multiple issues, but the most common effects include:
- Slow or unresponsive applications.
- The VM, mouse and/or keyboard freeze.
- Scrolling causes window staggers or jumps.
- Issues become worse when additional browser tabs or processes are spawned.
- Overall performance is poor.
See also: Advice for Systems with Low RAM.
Free up Additional Memory Resources
[edit]If a VM needs additional memory, then free up resources and/or add more RAM to the VM:
- Terminate any non-essential processes on the host.
- Shut down any non-essential VM.
- Shut down and/or close non-essential processes and browser tabs in Kicksecure VM.
To add additional RAM to the Kicksecure VM, follow the platform-specific advice below.
KVM
[edit]1. Shutdown the virtual machine(s).
virsh -c qemu:///system shutdown <vm_name>
2. Increase the maximum memory.
virsh setmaxmem <vm_name> <memsize> --config
3. Set the actual memory.
virsh setmem <vm_name> <memsize> --config
4. Restart the virtual machine(s).
virsh -c qemu:///system start <vm_name>
Kicksecure-Qubes
[edit]Utilize Qube Manager:
Qube Manager→VM_name→Qubes settings→Advanced→Max memory:mem_size
VirtualBox
[edit]- To add RAM in VirtualBox the VM must first be powered down.
Virtual machine→Menu→Settings→AdjustMemory slider→Hit: OK
See also: VirtualBox/Troubleshooting.
Generic Bug Reproduction
[edit]TODO
related: Generic Bug Reproduction
System Logs
[edit]Check Systemd Journal Log of Current Boot
[edit]To inspect the systemd journal log of the current boot, run:
sudo journalctl -b
This command requires pressing arrow keys like ↑, ↓, ←, →, as well as PgUp and PgDn for scrolling.
For convenient reading of the log (until the command is issued), the log can be dumped to file. For example, the following command would write the log to file ~/systemd-log.
sudo journalctl -b > ~/systemd-log
Use any available editor to read the log file, such as mousepad.
mousepad ~/systemd-log
Watch Systemd Journal Log of Current Boot
[edit]It is possible to watch the systemd journal log as it is written.
sudo journalctl -b -f
Check Systemd Journal Log of Previous Boot
[edit]It is possible to inspect the systemd journal log of the previous boot.
sudo journalctl -b -1
This command requires pressing arrow keys like ↑, ↓, ←, →, as well as PgUp and PgDn for scrolling.
For convenient reading of the log (until the command is issued), the log can be dumped to file. For example, the following command would write the log to file ~/systemd-log-previous.
sudo journalctl -b -1 > ~/systemd-log-previous
Use any available editor to read the log file, such as mousepad.
mousepad ~/systemd-log-previous
View List of Systemd Journal Logs
[edit]sudo journalctl --list-boots
Daemon Log View
[edit]To view the log of a specific systemd unit, use the following syntax:
(Replace unit-name with the actual name of the systemd unit.)
sudo journalctl -b --no-pager -u unit-name
Example:
sudo journalctl -b --no-pager -u sdwdate
Daemon Log Follow
[edit]To follow the log of a specific systemd unit, use the following syntax:
(Replace unit-name with the actual name of the systemd unit.)
sudo journalctl -f -b --no-pager -u unit-name
Example:
sudo journalctl -f -b --no-pager -u sdwdate
Daemon Status
[edit]To view the status of a specific systemd unit, use the following syntax:
(Replace unit-name with the actual name of the systemd unit.)
sudo systemctl status --no-pager unit-name
Example:
sudo systemctl status --no-pager sdwdate
Check Systemd Journal Log of Failed Boot
[edit]An alternative to recovery mode might be virtual consoles, since they are an easier and more lightweight solution. A virtual console login might still be possible when the graphical user interface no longer starts.
Prerequisite knowledge: Virtual Consoles. Try to log in to a virtual console in a functional VM as an exercise. If that works, try a virtual console login in the broken VM.
If a virtual console is unavailable:
- Boot into Recovery Mode
- Reboot into normal mode so a log for the failed boot will be written (if not previously enabled).
- Boot into recovery mode again.
- Check Systemd Journal Log of Previous Boot.
A dracut emergency shell may also be useful in case recovery mode is broken.
Slow Shutdown Issues
[edit]To help diagnose slow shutdown issues, enable the check-user-slice-on-shutdown.service systemd unit. [5]
sudo systemctl enable check-user-slice-on-shutdown.service
Permission Fix
[edit]Open a terminal.
Select your platform.
Kicksecure USER Session
If you are using a graphical Kicksecure with LXQt, complete the following steps.
Start menu → System Tools → QTerminal
Kicksecure SYSMAINT Session
In the System Maintenance Panel, under the Misc section, click Open Terminal.
Kicksecure-Qubes
If you are using Kicksecure-Qubes, complete the following steps.
Qubes App Launcher (blue/grey "Q") → Kicksecure App Qube (commonly named kicksecure) → QTerminal
sudo chown --recursive user:user /home/user
Hardware Issues
[edit]General Recommendations
[edit]Rhetorical questions:
- When was the last time a qualified person disassembled your computer/notebook and removed dust from the fan and checked the cooling system of the CPU?
- How often should maintenance be performed?
- What is your CPU temperature under heavy system load?
- What is the room temperature where the computer is operating?
Recommendations:
- Ensure your computer or notebook has regular, proper maintenance.
- Monitor CPU temperature by utilizing relevant host operating system tools.
- Consider cooling the room where computers/notebooks operate.
- Better placement (more air space) around computers or notebooks can help.
- Consider a passive or active (notebook) cooling pad. [6]
- Run
memtest86+to rule out RAM problems.
None of these issues are related to Kicksecure. Therefore, please do not ask these questions in Kicksecure support channels (until there is a Kicksecure Host DVD available) as per Self Support First Policy.
memtest86+
[edit]1. Install the memtest86+ tool.
On Debian (based) hosts such as Kicksecure.
Install package(s) memtest86+ following these instructions:
1 Platform specific notice.
- Kicksecure: No special notice.
- Kicksecure-Qubes: In Template.
2 Update the package lists and upgrade the system.
sudo apt update && sudo apt full-upgrade
3 Install the memtest86+ package(s).
Using apt command line --no-install-recommends option is in most cases optional.
sudo apt install --no-install-recommends memtest86+
4 Platform specific notice.
- Kicksecure: No special notice.
- Kicksecure-Qubes: Shut down Template and restart App Qubes based on it as per Qubes Template Modification.
5 Done.
The procedure of installing package(s) memtest86+ is complete.
For other host operating systems, refer to memtest86+ upstream documentation.
2. Reboot.
3. Start memtest86+ from (grub) boot menu.
4. Keep memtest86+ running for a significant period.
This should be run for as long as practically possible; for example, ideally overnight or for 8+ hours.
5. Check the memtest86+ output.
If there are any issues, red error messages appear in the middle of the screen.
6. Done.
The memory test is complete.
If memtest86+ identified any issues, these can manifest in various ways such as system crashes at random times. In such cases, the only likely solution is replacing the faulty hardware (RAM banks). [7]
Hard Drive Health Check
[edit]TODO: document this.
also known as S.M.A.R.T
- smartmontools
- gsmartcontrol
- smart-notifier
- nvme-cli
- package: gnome-disk-utility run: gnome-disks
- https://packages.debian.org/bookworm/lm-sensors

- https://packages.debian.org/bookworm/plasma-disks

- https://packages.debian.org/bookworm/psensor

- https://wiki.debian.org/SystemMonitoring

See Also
[edit]- Advice for Systems with Low RAM
- VirtualBox Troubleshooting
- KVM Troubleshooting
- Recovery Mode
- System Recovery using SysRq Key
- Core Dumps
Footnotes
[edit]- ↑
- Question: Why does it happen with Kicksecure ISO but not with Debian or some other ISO?
- Answer: The reason is unclear. Maybe a race condition. Or perhaps the premise might be wrong. A web search for this error message shows running Ubuntu and attempting to flash a Windows 10 ISO using KDE ISO Image Writer

failed. Also flashing KDE Neon failed

. This error seems to be reproducible with many Linux distributions. It is probably only possible for the KDE ISO Image Writer developers to fix this bug. There is probably nothing that the Kicksecure ISO could do better.
- Answer: The reason is unclear. Maybe a race condition. Or perhaps the premise might be wrong. A web search for this error message shows running Ubuntu and attempting to flash a Windows 10 ISO using KDE ISO Image Writer

- Question: Why does it happen with Kicksecure ISO but not with Debian or some other ISO?
- ↑
This procedure was useful for Kicksecure for Qubes R3.2 users, although the Qubes bug report is now resolved: https://github.com/QubesOS/qubes-issues/issues/2141

- ↑ 3.0 3.1 This process can be lengthy.
- ↑
"user support template": https://forums.whonix.org/t/workstation-keeps-freezing/7693/6

- ↑
https://github.com/Kicksecure/usability-misc/blob/master/usr/lib/systemd/system/check-user-slice-on-shutdown.service

- ↑ Perform thorough research beforehand.
- ↑ RAM bank warranties may apply.

We believe security software like Kicksecure needs to remain Open Source and independent. Would you help sustain and grow the project? Learn more about our 13 year success story and maybe DONATE!